Cacl2 Na3po4 Ca3 Po4 2 Nacl
New Snow
May 10, 2025 · 5 min read
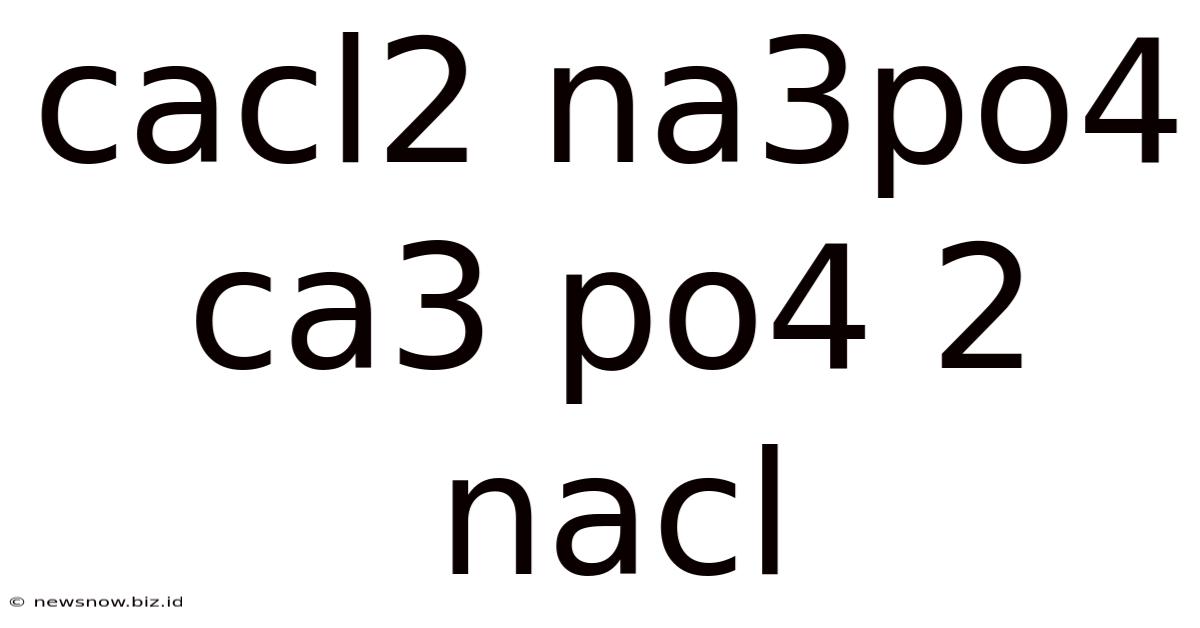
Table of Contents
The Double Displacement Reaction Between Calcium Chloride and Trisodium Phosphate: A Deep Dive
The reaction between calcium chloride (CaCl₂) and trisodium phosphate (Na₃PO₄) is a classic example of a double displacement reaction, also known as a metathesis reaction. This reaction leads to the formation of calcium phosphate (Ca₃(PO₄)₂) and sodium chloride (NaCl), a common salt. Understanding this reaction involves exploring its stoichiometry, the properties of the reactants and products, and the various applications of this chemical process.
Understanding the Reactants: CaCl₂ and Na₃PO₄
Before delving into the reaction itself, let's examine the individual properties of the reactants: calcium chloride and trisodium phosphate.
Calcium Chloride (CaCl₂)
Calcium chloride is an inorganic salt that appears as a white crystalline solid at room temperature. It's highly soluble in water, readily absorbing moisture from the air (hygroscopic), and often used as a desiccant. Its applications are numerous, spanning diverse fields:
- De-icing agent: CaCl₂'s ability to lower the freezing point of water makes it effective in de-icing roads and pavements during winter.
- Food additive: It functions as a firming agent and stabilizer in food processing. Its E number is E509.
- Construction: Used in concrete mixes to accelerate setting time and improve workability.
- Medicine: In some cases, it's used as a calcium supplement.
Trisodium Phosphate (Na₃PO₄)
Trisodium phosphate, also known as TSP, is another inorganic salt appearing as a white, crystalline powder. It's highly soluble in water and exhibits strong alkalinity. Its applications are similarly broad:
- Cleaning agent: TSP's strong alkalinity makes it an effective cleaning agent for removing grease, grime, and mildew. However, due to environmental concerns, its use is now somewhat restricted.
- Water softener: Its ability to chelate metal ions makes it a useful water softener.
- Food additive: It is occasionally used as a food additive, though its use is regulated.
The Reaction: CaCl₂ + Na₃PO₄ → Ca₃(PO₄)₂ + NaCl
The reaction between calcium chloride and trisodium phosphate is a double displacement reaction where the cations (Ca²⁺ and Na⁺) and anions (Cl⁻ and PO₄³⁻) exchange partners. The balanced chemical equation is:
3CaCl₂(aq) + 2Na₃PO₄(aq) → Ca₃(PO₄)₂(s) + 6NaCl(aq)
This equation reveals that three moles of calcium chloride react with two moles of trisodium phosphate to produce one mole of calcium phosphate and six moles of sodium chloride. Notice that calcium phosphate (Ca₃(PO₄)₂) precipitates out of the solution as a solid (indicated by (s)), while sodium chloride remains dissolved in the aqueous solution (indicated by (aq)). This precipitation is the driving force behind the reaction.
Understanding the Products: Ca₃(PO₄)₂ and NaCl
Let's now consider the properties of the products formed in this reaction:
Calcium Phosphate (Ca₃(PO₄)₂)
Calcium phosphate is an inorganic compound found in various forms, including hydroxyapatite, the main mineral component of bones and teeth. Its different forms exhibit varying solubility in water. The form produced in this reaction, however, is generally insoluble. Key properties include:
- Low solubility: This characteristic is crucial in the reaction, as it drives the formation of the precipitate.
- Biocompatibility: Its presence in bones and teeth highlights its biocompatibility and use in biomedical applications.
- Applications: It finds use as a fertilizer, dietary supplement, and in various industrial processes.
Sodium Chloride (NaCl)
Sodium chloride, commonly known as table salt, is a ubiquitous compound with numerous applications:
- Food seasoning: Its primary role is as a seasoning and flavor enhancer in food.
- Food preservation: Salt has been used for centuries to preserve food by preventing microbial growth.
- Industrial applications: Used extensively in various industrial processes, from chemical manufacturing to water treatment.
Stoichiometry and Calculations
The balanced chemical equation is fundamental to understanding the stoichiometry of this reaction. It allows us to perform calculations, for example, determining the amount of product formed given a certain amount of reactant.
Example: If we have 10 grams of CaCl₂, how much Ca₃(PO₄)₂ will be produced?
-
Convert grams of CaCl₂ to moles: The molar mass of CaCl₂ is approximately 110.98 g/mol. Therefore, 10 g CaCl₂ is equal to 10 g / 110.98 g/mol ≈ 0.09 moles CaCl₂.
-
Use the mole ratio: According to the balanced equation, 3 moles of CaCl₂ produce 1 mole of Ca₃(PO₄)₂. Therefore, 0.09 moles CaCl₂ will produce (0.09 moles CaCl₂ * 1 mole Ca₃(PO₄)₂ / 3 moles CaCl₂) ≈ 0.03 moles Ca₃(PO₄)₂.
-
Convert moles of Ca₃(PO₄)₂ to grams: The molar mass of Ca₃(PO₄)₂ is approximately 310.18 g/mol. Therefore, 0.03 moles Ca₃(PO₄)₂ is equal to 0.03 moles * 310.18 g/mol ≈ 9.3 grams Ca₃(PO₄)₂.
This calculation demonstrates how the stoichiometry governs the quantities involved in the reaction. Similar calculations can be performed for other reactants and products.
Applications of the Reaction
The reaction between calcium chloride and trisodium phosphate has several practical applications, many stemming from the properties of the products:
- Wastewater treatment: The precipitation of calcium phosphate can be exploited in wastewater treatment to remove phosphate ions, which are responsible for eutrophication in water bodies.
- Synthesis of calcium phosphate: This reaction offers a straightforward method for synthesizing calcium phosphate, a material with diverse applications in biomaterials, fertilizers, and other industries.
- Educational purposes: The reaction is often used in educational settings to demonstrate double displacement reactions, precipitation reactions, and stoichiometric calculations.
Safety Considerations
When handling chemicals involved in this reaction, it's essential to observe safety precautions:
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE): This includes safety goggles, gloves, and a lab coat.
- Work in a well-ventilated area: Avoid inhaling dust or fumes produced during the reaction.
- Dispose of waste properly: Follow local regulations for disposing of chemical waste.
Conclusion
The reaction between calcium chloride and trisodium phosphate is a fundamental chemical process with important implications in various fields. Understanding its stoichiometry, the properties of the reactants and products, and safety precautions is essential for its safe and effective application. The reaction's ability to produce insoluble calcium phosphate makes it particularly useful in applications requiring phosphate removal or the synthesis of this valuable compound. Further exploration of this reaction can lead to innovative applications in areas such as environmental remediation and materials science. The principles illustrated here – double displacement reactions, precipitation, and stoichiometry – are cornerstones of chemistry and crucial for understanding numerous other chemical processes.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Cacl2 Na3po4 Ca3 Po4 2 Nacl . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.